VPS vs VPN: Is A VPN better than a VPS?
VPS and VPN are similar in spelling, but they are two different concepts and have completely different purposes, whether in use or functionality.
Many internet users mix these technologies up or wonder if one can replace the other. A VPS (Virtual Private Server) functions like a private computer, and a VPN acts as a shield. While both enhance your online experience, they solve different problems overall.
In this comprehensive guide, we explain exactly what VPS and VPN technologies are, how they differ, and which one might be right for your specific needs. So be with us.
What is a VPS (Virtual Private Server)?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is essentially a virtualized part of a physical server in a data center. Think of it as if you were renting an apartment in a building instead of buying the entire property.
How VPS Works
When you Buy VPS hosting, you get a dedicated portion of server resources (CPU, RAM, storage) that operates independently of other users on the same physical machine.
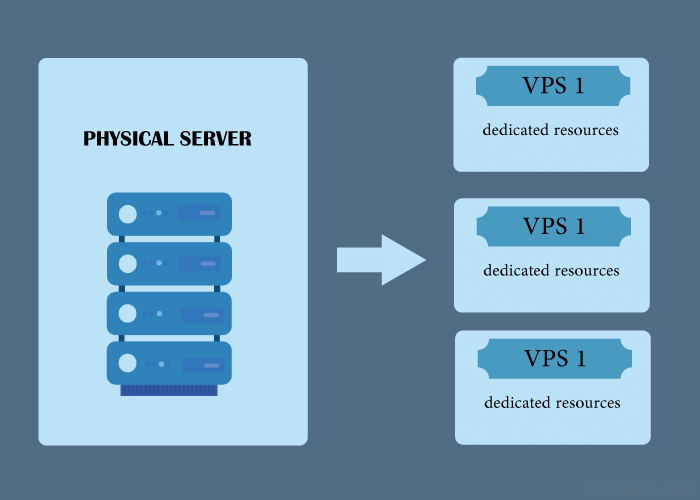
This creates your own “virtual” server with:
- A dedicated operating system
- Root access for complete control
- Allocated resources that aren’t shared with other users
- The ability to install any software you want
Common VPS Use Cases
- Website hosting: operation of resource-intensive websites or multiple websites
- Application development: testing and deploying applications
- Customized server applications: Email servers, database servers, etc.
- Game servers: Hosting of multiplayer gaming environments
- Remote desktop environment: A virtual computer that you can access from anywhere
What Is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
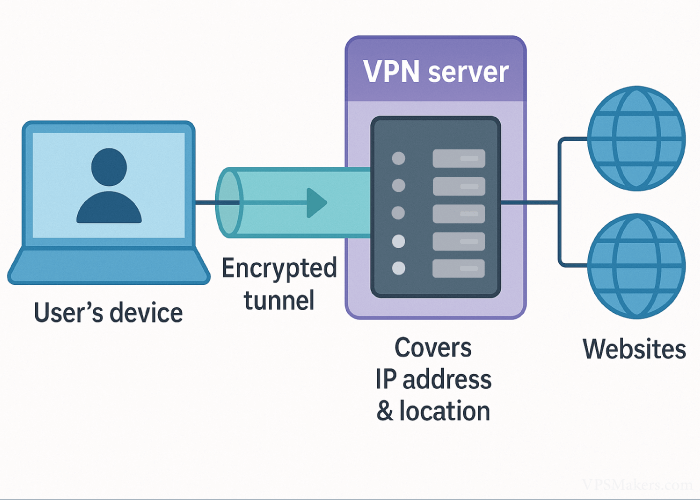
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a cybersecurity tool that creates an encrypted “tunnel” between your device and a VPN server that masks your IP address and protects your data. It ensures privacy, anonymity and protection against espionage while allowing secure access to local content worldwide.
When should you use a VPN?
We come to the conclusion that VPN has several uses in the world of technology. But here we will explain four of them.
- Secure access: Preventing ISPs, websites and advertisers from tracking you, encrypting your connection on unsecured networks
- Bypassing geo-restrictions: Accessing content that is restricted to certain regions
- Avoid bandwidth throttling: Prevent your ISP from throttling certain services
- Remote working security: Secure access to company resources from outside the office
How does a VPN work?
The connection redirects your internet traffic via a remote server and secures the data travelling between you and the VPN server after installation a VPN app or software and enabling it. In plain language, a VPN creates an encrypted tunnel for the user’s online traffic. It wraps each data packet in an outer packet and encrypts it.
The key difference between VPN & VPS
VPNs and VPSs may seem similar but there are significant differences between them. In this article, we will highlight the five key distinctions between VPNs and VPSs, accompanied by a table to provide a clearer understanding.
| Feature | VPS (Virtual Private Server) | VPN (Virtual Private Network) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hosting websites, applications, or services | Enhancing privacy and security while browsing |
| What It Provides | Computing resources and storage | Encrypted connection and IP masking |
| Technical Expertise Required | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Typical Monthly Cost | $5-$100+ depending on resources | $3-$12 per month |
| Control Level | Full root/admin access | Limited to connection settings |
| Maintenance Required | Regular updates and security management | Minimal; handled by provider |
| Primary Users | Developers, businesses, tech enthusiasts | General internet users, remote workers, travelers |
1-Security
A VPS separates your virtual resources from other users on the same physical server. So, this enhances the overall security level. Your data won’t be affected if another user’s website or application becomes compromised. A VPN provides security by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet connection. So, hacking your data will be more difficult for phishing criminals or some of the government agencies.
2-Speed
A VPS can provide better speed and reliability than a VPN. When it comes to speed, uptime, and performance, a VPS can be the winner. Because a VPS is a dedicated virtual machine, but a VPN routes your traffic through a remote server. The routing through a remote server can add little latency to the network function. Regardless, the VPN performance can change based on the service quality provided by your VPN company and the distance between you and the server.
3- Price
A VPS can be more expensive than a VPN because it is a more specialist service. Buying a VPS profits our business, and this can justify the investment.
4- Flexibility
VPS provide more control and customization than VPN. In VPS, you have your own virtualized computer environment, and you can install any software on your operating system and configure the server as you wish. VPNs are a little bit limited in regards to what you can do. Some VPNs allow you to choose which server or location to connect to, but not all VPNs have the same level of control, customization, and flexibility.
5- Storage
Users can buy a VPS as a remote storage location to securely store and backup their important files and data wherever and whenever. Because each VPS has its exclusive resources, like CPU capacity, Ram, and Disk Storage. VPNs doesn’t have the storage and backup option.
Can you utilize VPS as a VPN?
The answer is yes. VPS services can also be used to build VPN services. But this can limit the advantages that come with full-service VPNs provided by VPN companies commercially.
Can You Use Both a VPS and a VPN Together?
Absolutely! In fact, they can complement each other beautifully:
- Host your business website on a VPS for performance and control
- Use a VPN when accessing your VPS admin panel from public Wi-Fi for added security
- Set up your own private VPN server on a VPS (for advanced users who need a customized VPN solution)
For many professionals, especially those in tech fields, using both tools makes perfect sense as part of a comprehensive digital strategy.
Conclusion
To wrap up, a VPS is a virtual private server bought from a hosting company for hosting other servers, including applications, websites, and games. However, a VPN is a service that lets users have private and secure online activity. You can change your virtual location and protect your data with just one click. So, internet users can increase their browsing security by just installing a VPN on their phones, tablets, laptops, and other electronic devices.

